MediaTek Wi-Fi Chips Hacked – CVE-2024-20017 Threat Alert
SonicWall’s threat research team has discovered a major security vulnerability, labeled CVE-2024-20017, affecting certain MediaTek Wi-Fi chipsets. This flaw is particularly dangerous because it requires no user interaction to exploit and has a severity score of 9.8 out of 10 on the CVSS 3.0 scale.
You might be interested in: Instagram Introduces New Safety Features for Teens
Affected Devices and Versions
The vulnerability impacts the MediaTek MT7622 and MT7915 Wi-Fi chipsets, as well as the RTxxxx SoftAP driver bundles. Products from well-known brands like Ubiquiti, Xiaomi, and Netgear that use these chipsets are at risk. Specifically, devices running MediaTek SDK version 7.4.0.1 and earlier, along with OpenWrt versions 19.07 and 21.02, are affected. This includes a wide range of routers and smartphones.
What Makes This Vulnerability Dangerous?
An attacker can exploit this flaw to execute code on the device remotely without any action from the user. The issue arises from an out-of-bounds write error caused by improper handling of data lengths in network packets. Essentially, the device can be tricked into overwriting parts of its memory, allowing an attacker to run malicious code.
Technical Details
The problem lies in a network service called wappd, which manages wireless interfaces and access points like Hotspot 2.0. This service communicates with different parts of the device using Unix domain sockets. The vulnerability occurs because wappd takes a length value from incoming network packets without properly checking it and uses it in a memory copy operation. This can lead to a buffer overflow, where data is written outside the intended memory area.
How Attackers Can Exploit This
To take advantage of this flaw, an attacker sends specially crafted network packets that include specific data structures expected by the device. These structures are named RT_IAPP_HEADER and RT_IAPP_SEND_SECURITY_BLOCK in the code. By manipulating the length values and the content of these packets, the attacker can cause the device to overwrite its own memory, leading to a stack buffer overflow of up to 1,433 bytes.
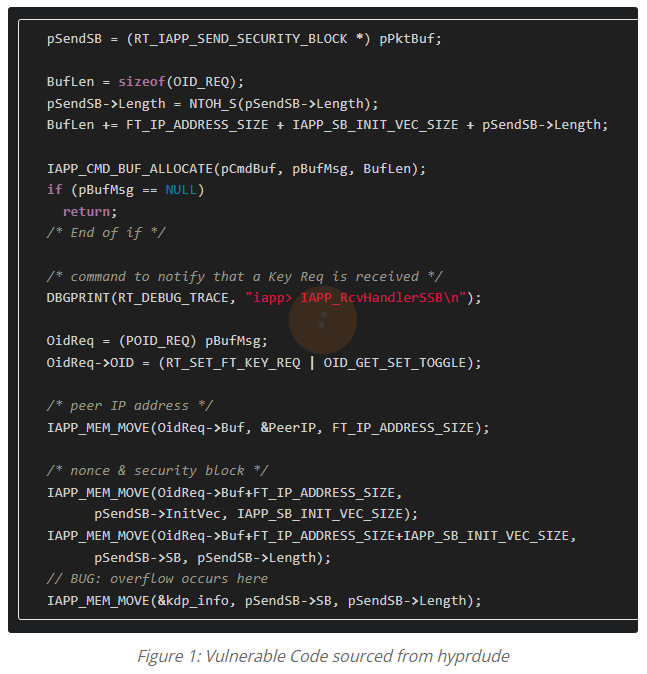
Public Exploit Code and Methods
There is publicly available code that demonstrates how to exploit this vulnerability. Attackers can use a technique called Return-Oriented Programming (ROP) to manipulate the device’s memory and execute arbitrary commands. This method can be used to launch a reverse shell, giving the attacker remote control over the device. Tools like bash and netcat are utilized in this process.
SonicWall’s Protective Measures
SonicWall has released security signatures to help protect against this vulnerability:
- IPS Signature 20322: MediaTek MT7915 Service Out-of-Bounds Write 1
- IPS Signature 20323: MediaTek MT7915 Out-of-Bounds Write 2 WLAN
These signatures can detect and block attempts to exploit this flaw.

What You Should Do
Given the seriousness of this vulnerability and the availability of exploit code, it’s crucial to update your devices immediately. MediaTek has released patches to fix this issue. Make sure to upgrade your device’s firmware to the latest version to protect yourself from potential attacks.
Conclusion
This vulnerability poses a significant risk to many devices due to its high severity and ease of exploitation. If you own a router or smartphone that uses the affected MediaTek chipsets, take immediate action by updating your firmware to ensure your device is secure.
Relevant Links
- https://corp.mediatek.com/product-security-bulletin/March-2024
- https://blog.coffinsec.com/0day/2024/08/30/exploiting-CVE-2024-20017-four-different-ways.html
- https://securityonline.info/cve-2024-20017-cvss-9-8-zero-click-exploit-discovered-in-popular-wi-fi-chipsets-poc-published/
- https://github.com/mellow-hype/cve-2024-20017/tree/main
