Remote Hacks Possible with Kia License Plates
Security Issues Could Have Allowed Remote Vehicle Control
Researchers have uncovered several significant security flaws in Kia vehicles that, before being fixed, could have allowed hackers to remotely control essential car functions using just a license plate. According to security experts Neiko Rivera, Sam Curry, Justin Rhinehart, and Ian Carroll, these attacks could be carried out in under 30 seconds on any Kia vehicle with the necessary hardware, regardless of whether it was enrolled in the Kia Connect subscription service.
You might be interested: MediaTek Wi-Fi Chips Hacked – CVE-2024-20017 Threat Alert
Vulnerabilities Affecting Most Kia Cars After 2013
The researchers found that nearly all Kia models manufactured after 2013 were impacted. These flaws could have exposed sensitive owner information such as their name, phone number, email, and home address. Worse, attackers could secretly add themselves as a second, invisible user of the vehicle, without the owner even knowing.
How the Flaws Worked
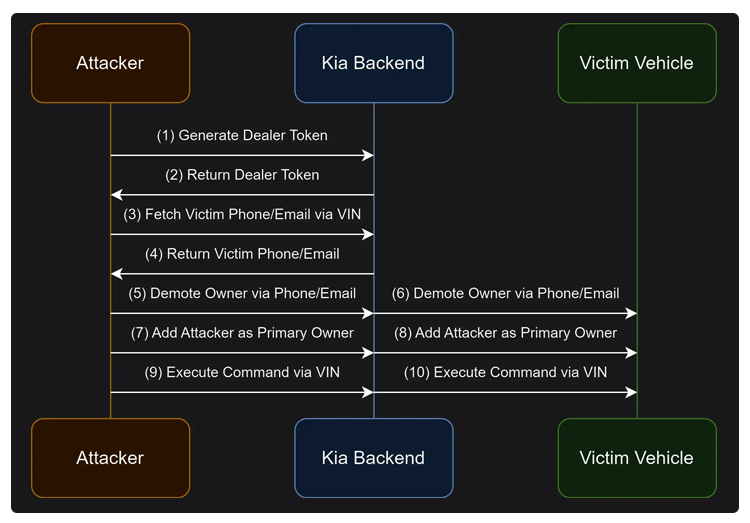
The security flaws were linked to Kia’s dealership infrastructure (“kiaconnect.kdealer[.]com”). Hackers could exploit this system to set up a fake account by sending an HTTP request and receiving access tokens.
With these tokens, they could then send another HTTP request to a dealer’s API gateway and, using the vehicle identification number (VIN), gain access to the car owner’s personal information, such as their name, phone number, and email address.
In just four simple HTTP requests, a hacker could also send remote commands to control various car functions.
Attackers Could Gain Control Without Alerting the Owner
Once an attacker gained access, they could add their email address as the primary account holder and give themselves control over the vehicle. Alarming as it sounds, car owners would not be notified about any changes to their account or vehicle.
Hackers could simply enter a car’s license plate number into a custom dashboard, and within 30 seconds, they’d be able to control features such as unlocking the car, starting the engine, or even honking the horn.
Kia Fixes the Flaw
The vulnerabilities were responsibly reported to Kia in June 2024, and the company rolled out a patch on August 14, 2024. To date, no real-world exploitation of these vulnerabilities has been detected.
Ongoing Risks in Car Security
“Just like social media companies like Meta can introduce bugs that compromise user accounts, car manufacturers can also introduce security flaws in their vehicles,” said the researchers.
The discovery highlights the growing concern over car security as modern vehicles become more connected and reliant on digital systems.
